Global Governance
Your Present Location: PROGRAMS> Global GovernanceThe promise of China`s G20 presidency
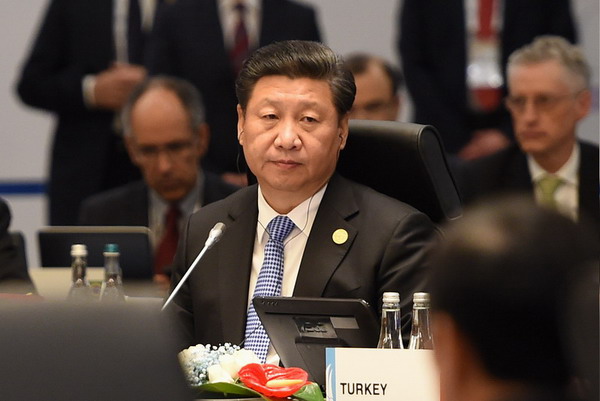

Chinese President Xi Jinping attends the first session of the 10th summit of the Group of Twenty (G20) major economies in Antalya, Turkey, Nov. 15, 2015. [Photo/Xinhua]
China has assumed the G20 presidency since Dec 1. Over the next year - and especially at the organization`s September summit, to be held in Hangzhou - China plans to help lay the groundwork for a world economy that is more "innovative, invigorated, interconnected, and inclusive." The question is how.
The G20 has gained some momentum, and China can benefit. If the current United Nations Climate Change Conference produces a binding global agreement to curb greenhouse-gas emissions, that momentum will become even stronger. Given that the G20 countries represent two-thirds of the world`s population and 85 percent of its GDP, they would be integral to the implementation of any deal. By providing a framework for these countries to meet regularly to discuss global challenges like climate change, the G20 - which is, at best, a club of self-selected members - gains legitimacy.
All of this bodes well for China`s capacity to help counter the global slowdown in growth, trade, and investment. And not a moment too soon: The ongoing slowdown is among the greatest risks the world currently faces, because it could exacerbate desperation and instability in already-fragile countries, while compelling more robust economies to turn inward, rather than address proliferating crises.
Fortunately, China has lately been showing its commitment to becoming a more responsible global stakeholder. Perhaps most notable, it recently led the establishment of the Beijing-based Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), which will serve largely as a vehicle for Chinese foreign investment.
Specifically, the AIIB will (among other things) provide funding for China`s ambitious Belt and Road Initiative, which aims to enhance trade linkages throughout Asia, across the Middle East, and into Europe, through massive infrastructure investment. The fact that more than 50 countries signed on as founding members indicates that members` interest in securing resources to meet urgent infrastructure trumps geopolitical competition.
The same brand of pragmatism was apparent in China`s response to its exclusion from the recently agreed Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) trade agreement, spearheaded by the US and including 12 Pacific Rim countries. Instead of grandstanding, China has shown its willingness to pursue different types of trade arrangements, as needed. If China can grasp the opportunity of the G20 presidency to broker a deal to conclude the World Trade Organization`s long-stalled Doha Development Round, its credentials as a global stakeholder would be enhanced.
There is more promising news. The Chinese renminbi has joined the US dollar, the British pound, the euro, and the Japanese yen in the basket of currencies that determines the value of the International Monetary Fund`s reserve asset, special drawing rights. With the renminbi moving one step closer to becoming a reserve currency, China`s capacity to help the world - and especially emerging-market economies - cope with impending market volatility will be greatly enhanced.
Building a robust, unified, and fast-growing global economy will be extremely difficult even under the most favorable circumstances. It will be impossible if large swaths of the world - most notably, the Middle East - remain mired in chaos and violence. Given this, China could, like Turkey, use its G20 presidency to promote consensus on the need to end the Syrian conflict and to support long-term peace and economic development throughout the Middle East by pursuing strategies that revive trade, investment, and employment.
Next year, the G20 has an important opportunity to show that it can deal effectively with global crises, from the risk of secular stagnation to the scourge of transnational terrorism. With the right mix of realism and power sharing, China`s G20 presidency could catalyze important progress - and perhaps even place a firm foundation beneath a new global economic architecture fit for the twenty-first century.
Andrew Sheng is distinguished fellow of the Asia Global Institute at the University of Hong Kong and a member of the UNEP Advisory Council on Sustainable Finance. Xiao Geng is director of the IFF Institute, and professor at the University of Hong Kong and a fellow at its Asia Global Institute.
Key Words: G20; China; promise




















































































 京公网安备 11010802037854号
京公网安备 11010802037854号





