Eco-finance
Your Present Location: PROGRAMS> Eco-financeMa Jun: Building a Green Financial System in China
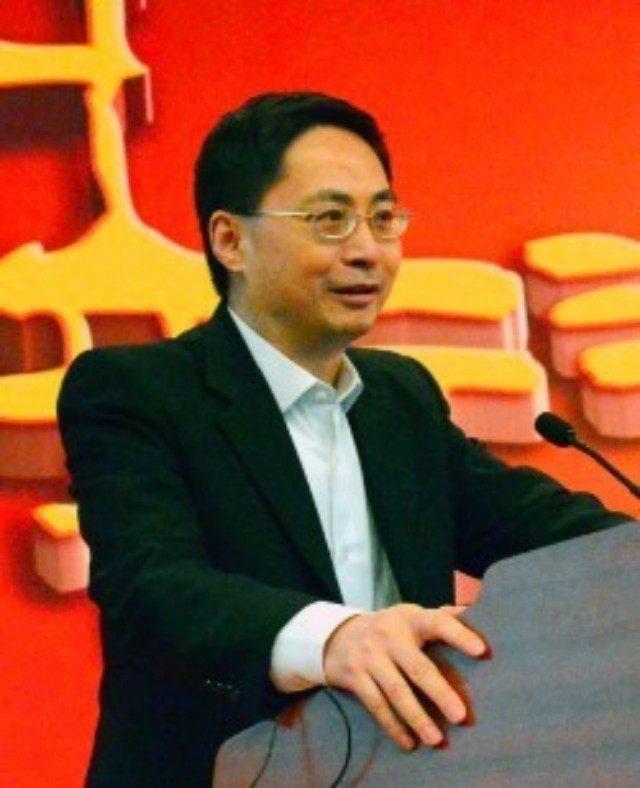

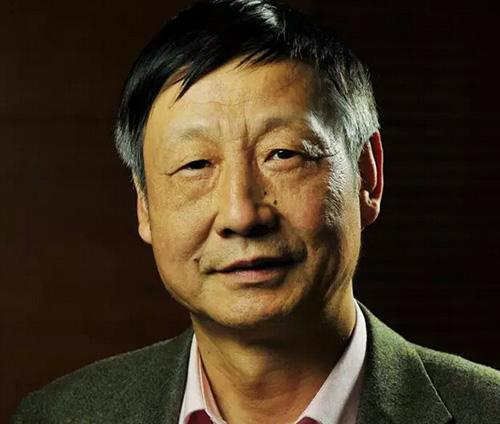
Dr. Ma Jun, chief economist of People’s Bank of China (PBC) Research Bureau, Executive Council Member of China Urban Financial Society, Editorial board member of Finance Forum.
Building a green financial system in China helps foster new economic growth points and promote green transformation of the economic structure. To divert more social funds into the green industries, we must increase the return over investment (ROI) of green projects while decrease that of polluting projects, enhance the awareness of corporate social responsibility, promote green investment and strengthen consumers’ awareness of environmental protection and green consumption.
I. The Necessity and Urgency for Building a Green Financial System
China is facing increasing environmental challenges. It is urgent to transform into the green and sustainable economic growth mode. The key to the green transformation is establishing mechanisms and systems that encourage green investment and restrain polluting investment. Environmental improvement in China calls for not only strong end-of-pipe control measures, but also fiscal, taxation and financial measures to reform the incentive mechanism for resource allocation so as to form cleaner and greener industrial, energy and transport structures. The incentive mechanism for allocation of resources, specifically funds (i.e. financial resources), will play a critical role. As long as funds are gradually withdrawn from polluting industries and channeled to green and environmentally-friendly industries, allocation of other resources including land and labor will be optimized. This requires China to establish a green financial system to strengthen the incentive mechanism for the input of financial resources, especially social funds, into green projects. To cope with environmental pollution, China is in urgent need to set up a “green financial system” to channel social funds to green projects for maximum social welfare.
II. Green Finance Will Help Stabilize Growth and Adjust the Structure
A green financial system consists of a series of policies, institutional arrangements and infrastructure that divert social funds to green industries such as environmental protection, energy saving, clean energy and clean transport by means of financial services including loan, private equity investment, bond and stock issuance, insurance and trade of emission rights. The green financial system will also play a major role in stabilizing growth and adjusting the structure, and help China improve its financial sustainability and its image as a responsible power.
First, it triggers new growth points and improves economic potential;
Second, it accelerates green transformation of industrial structure, energy structure and transport structure and increases the technical content of economy;
Third, it mitigates financial pressure from environmental challenges;
Fourth, it builds up China’s image as a responsible power.
III. Theoretical Framework of Green Financial Policy
To divert more social funds to green industries, China may start from the following:
1. to increase the ROI of green projects while decrease that of polluting projects. The following policies may be taken: first, to raise the price and ROI of clean products, and reduce the price subsidy and ROI of polluting products; second, to reduce the tax and other costs of clean products (e.g. to cut the financing cost to facilitate financing) so as to raise the ROI, and increase the tax and other costs of polluting products so as to lower the ROI.
2. to strengthen the awareness of corporate social responsibility (CSR) so as to boost green investment. Compared with the above policies, it can produce more effects with less cost.
3. to build up consumers’ awareness of environmental protection and green consumption, so as to affect the market price by changing consumers’ preference and minimize externality.
IV. Advice on Building a Green Financial System in China
Based on the aforementioned theoretical framework as well as international experience and the reality in China, the following 14 suggestions are herby presented:
i. Advice on institutional construction which is the organizational basis for green investment:
The green banking system should be established to give full play to the expertise, economy of scale and risk control advantage of green banks in green credit and investment;
2. The green industrial fund is a platform where social funds can be spent on specialized green investment, and from the perspective of fund source, is an important supplement to green credit. The development of the green industrial fund in the PPP mode should be promoted to attract private fund and equity investment with limited government funds. Policies in favor of individual PPP projects should be generally applicable to the industrial fund in the PPP mode.
3. Foreign investment and development institutions, such as the Silk Road Fund, Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank and New Development Bank, should announce their participation or, in reference to the Equator Principles, establish a high-standard (not lower than that of World Bank and Asian Development Bank) environmental risk management system for full information disclosure and vigorous promotion of foreign green investment.
ii. Advice on fiscal and financial policies
1. The interest discount mechanism for green loans with government funds should be improved to give higher discount, gradually lift the discount bar, make reasonable discount terms, streamline approval procedures, and make trial implementation of green loan discount management by the eco-finance departments of policy banks, green banks or commercial banks as entrusted by fiscal authorities.
2. It is advised that competent authorities should issue guidance on green bonds, allow and encourage banks and enterprises to issue green bonds to provide long-term, low-cost fund sources for green loans and green investment.
3. The mechanism in favor of green enterprises in the stock market should be enhanced. The certification standards for green industries and green enterprises should be defined, the IPO approval and registration procedures for green enterprise should be streamlined, the limits for the amount and proportion of fund raised to supplement the working capital or repay bank loans of green enterprises be loosened as appropriate, and priority be given to eligible green enterprises listed on the National Equities Exchange and Quotations (NEEQ) in IPO transfer.
iii. Advice on financial infrastructure in favor of green investment
1. The construction of the emission rights trade market should be accelerated. Based on enhanced legislation and top-level design, efforts should be made to accelerate the construction of the national carbon trade market to rationally plan the quota and trade mechanism, give full play to the incentive role of price in emission reduction, and improve market liquidity.
2. The green rating system should be formed to give green enterprises and projects more favorable rating and reduce their financing cost. Based on proper rating standards and measures, rating firms may introduce double rating to green rating pilot programs, and commercial banks and the Credit Reference Center of The People’s Bank of China should also study and develop green rating.
3. The development and application of green stock index should be promoted to guide the capital market to invest more in green industries. The development and innovation of the green index should be promoted to strengthen the representativeness of green index, and institutional investors should be encouraged to use the green index for investment and develop more targeted and diversified sustainable green investment products.
4. The Ministry of Environmental Protection and financial societies (associations) should take the lead in establishing the non-for-profit environmental cost accounting system and database to improve the accessibility of environmental assessment methods and data and reduce the investors’ green project assessment cost.
5. The green investors network should be established. Financial societies (associations) with government background and influential financial institutions should appeal and initiate the green investors network to supervise the fulfillment of environmental responsibilities of the invested enterprises, foster the green investment ability of institutional investors and launch education on green consumption.
iv. Advice on building the legal and regulatory system in favor of green finance
1. Compulsory green insurance should be applied to more sectors in order to restrain polluting investment and provide environmental restoration funds through the insurance market mechanism.
2. The environmental legal responsibilities of banks should be clarified; victims should be allowed to sue the financial institutions which give loans to and are jointly responsible for polluting projects.
3. CSRC and stock exchanges should establish the mechanism for compulsory environmental information disclosure by listed companies, to serve as the basis for environmental risk assessment and accurate valuation of these listed companies and guide the capital market to allocate more funds to green industries.
This article originally published in the fifth issue of Financial Forum in 2015
Key Words: Green Financial; economist; think tank




















































































 京公网安备 11010802037854号
京公网安备 11010802037854号





