Picture
Your Present Location: HOME> PictureLecture on 40 years of Chinese economy held in RDCY
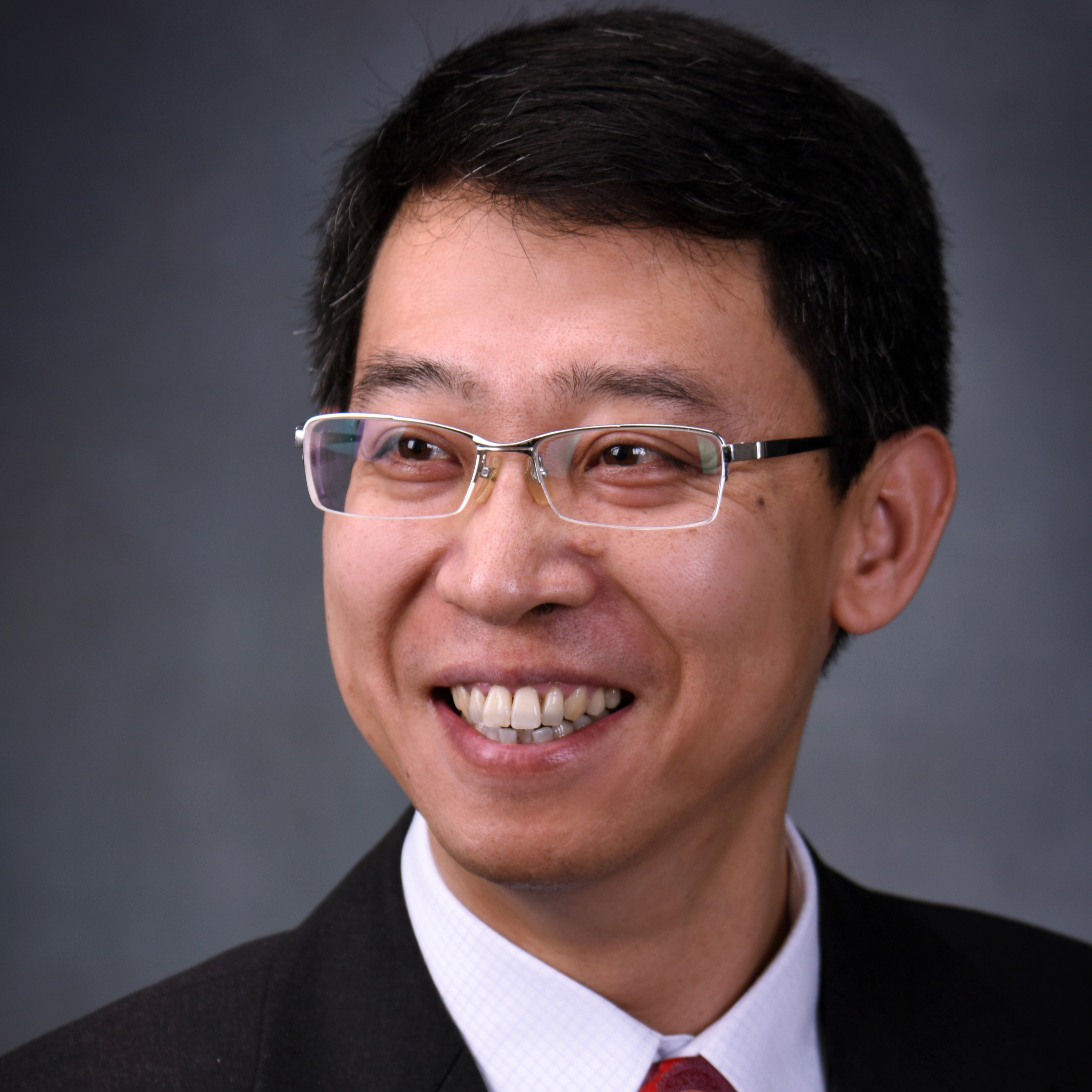
On the evening of December 18th, RDCY series lecture themed “the 40th anniversary of reform and opening up” was held at Chongyang Institute for Financial Studies at Renmin University of China (RDCY). Chen Yanbin, the Vice Dean of the School of Economics at Renmin University of China, delivered a speech entitled 40 years of Chinese economy, focusing on the current macroeconomic and financial situations. The lecture was presided over by Chen Chenchen, a research fellow at RDCY. Jia Jinjing, assistant to the dean, made an introductory speech.
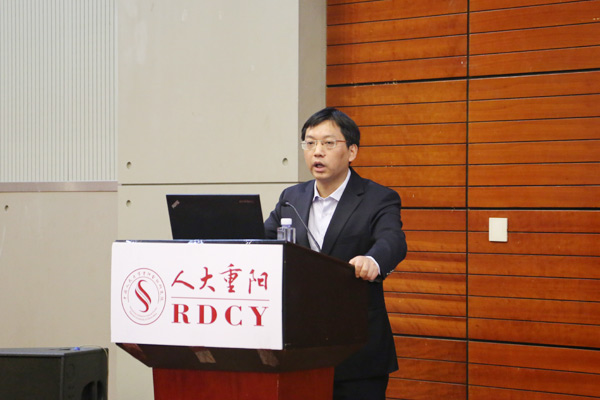

Professor Chen Yanbin pointed out that the current Chinese economy needs to increase macroeconomic policies and strengthen policy coordination. He believes that China's economic growth rate has slowed down in 2018, and downward pressure has increased. With specific data, he made detailed analysis from the perspective of total demand structure--consumption, investment and export. Furthermore, major economies such as the United States, Japan and Europe have shown a phenomenon of growth differentiation and a gradual decline in unemployment.
Then, Professor Chen introduced the six major financial risks that are common in theory, namely foreign exchange risk, asset price volatility risk, high debt risk, credit risk, liquidity risk and improper financial innovation risk. He believes that some financial risks in China have improved in 2018, such as liquidity risks and improper financial innovation risks. However, some financial risks have increased. Overall, China's financial stability is currently in a safe and controllable state, and the overall stability of the financial system needs to be guarded.
Professor Chen evaluated China's macroeconomic policies from monetary policy and fiscal policy. He believes that if the two aspects can strengthen coordination, the economic operation may be better.

Finally, according to China's current economic situation, Professor Chen suggested to increase macroeconomic policies and strengthen macroeconomic policy coordination, especially to strengthen the coordination of monetary and fiscal policies and the coordination of macroeconomic policies and economic growth policies. The optimal policy combination adopted from a large macro perspective is to take into account both short-term economic stability and long-term growth and high-quality development, so as to help cope with the difficulties confronted in economic development and promote the steady development of Chinese economy.




















































































 京公网安备 11010802037854号
京公网安备 11010802037854号





