Picture
Your Present Location: HOME> PictureReport on the Global Use of Covid-19 Vaccines was successfully published
Editor’s Notes:
The Boao Forum for Asia Academy Secretariat had published the report on the Global Use of Covid-19 Vaccines successfully on July 29 from 10:00-10:45 in Beijing.
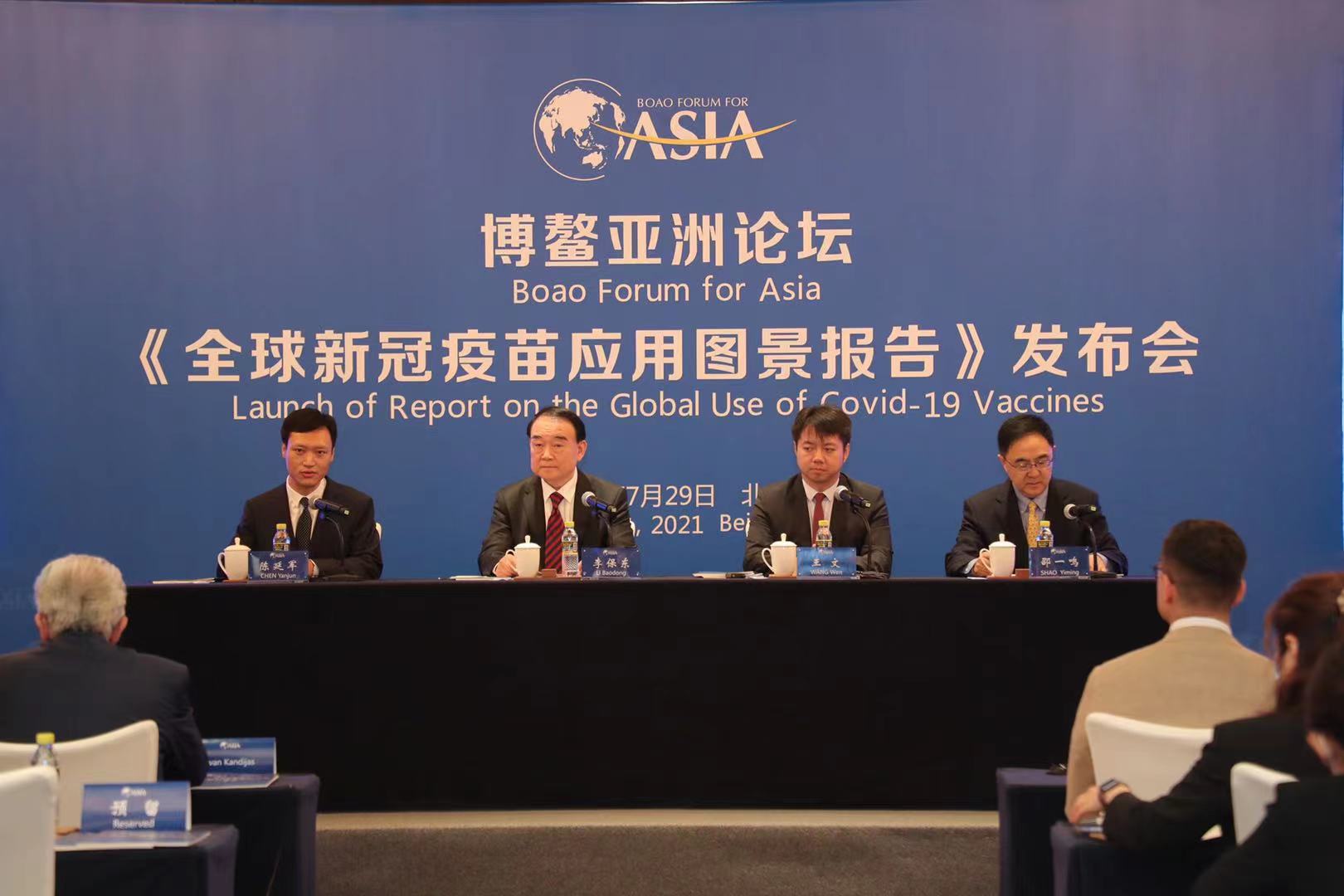

The Global Use of Covid-19 Vaccines Report, written by both Boao Forum for Asia Academy and Chongyang Institute for Financial Studies of Renmin University of China(RDCY), presents a comprehensive picture of the application of the Covid-19 vaccines from a global perspective in terms of its research and development, production, application, effectiveness and prospects. Report was published by Mr. Li Baodong, Secretary-General of the Boao Forum for Asia, Wang Wen, executive dean of RDCY, and other representatives of international organizations, ambassadors of relevant countries and experts in the field of vaccines were invited to participate in the meeting.

Click the link below for the English version of the report.
Follows are the Core Views of the Report on the Global Use of Covid-19 Vaccines:
1 An Overview on the Global Vaccine Development
1.1 With the accelerated development of the COVID-19 vaccines, the strong regulatory requirements of e very government have provided effective guarantees of vaccine safety.
1.2 China and other emerging economies have once again joined in the emergency vaccine development.
1.3 Enterprises in different countries have demonstrated amazingly high efficiency in vaccine manufacturing.
2 Vaccinations in different countries
2.1 The uneven distribution of vaccines in the international community. The vaccination rate in underdeveloped countries and regions is generally low.
2.2 China is expected to complete vaccination of at least 70% of the target population by the end of 2021.
2.3 Western developed countries generally lead other countries in vaccination rates, but they have not yet fully reached the herd immunity threshold.
2.4 The vaccination rate in Japan is much lower than that of developed, it has not led in the development of COVID-19 vaccines.
3 Impact of vaccine application on pandemic control
3.1 Aim: Achieving universal vaccination
3.2 Vaccines have shown obvious effects in curbing the pandemic.
3.3 As long as the “immunization gap” between underdeveloped countries and developed countries still exists, the world will still face public health risks.
3.4 The implement of the “vaccine passport” mechanism.
4 Policies and actions of major countries on the international distribution of vaccines
4.1 China's vaccine aid and exports have exceeded the total of other countries, with developing countries constituting the primary export destinations.
4.2 US: Global concern is rising that they United States has stockpiled a huge quantity of vaccines, yet there is a gap between its capability and how many it has provided to others around the world.
4.3 EU countries: The vaccine distribution policy of EU countries aims to ensure the internal vaccination rate of EU member states. Exports of vaccines mainly go to middle income and high - income countries.
4.4 The Group of Seven (G7) summit promised to donate 1 billion doses of COVID-19 vaccines to poor countries by the end of 2022. However, this is still far from the global demand for vaccines.
5 The International Vaccines Coordination Mechanism
5.1 EUL (Emergency Use Listing)
5.2 COVAX (COVID-19 Vaccines Global Access)
5.3 EUL and COVAX are not mandatory for governments from all countries. the international community urgently needs to establish a fair and efficient international vaccine distribution mechanism to ensure the universal supply of vaccines on a global scale.
6 The Impact of Vaccine Use on International Relations
6.1 The application and distribution of COVID-19 vaccines have become a prominent issue in international relations.
6.2 Propositions and actions on the international distribution of vaccines have an impact on the soft power and international image of countries.
6.3 International discussions on vaccine allocation have highlighted different views on the private and public attributes of vaccines.
6.4 China’s position of making vaccines a "global public goods" is more in line with the multilateralism called for by the WHO.
6.5 The “vaccine diplomacy” argument is the latest manifestation of the politicization of the fight against the pandemic manifestation of the politicization of the fight against the pandemic.
6.6 The “vaccine diplomacy” argument also reflects the trend of ideologicalization in international relations.
7 Recommendations for the International Community
7.1 First,Countries should always keep increasing vaccination rates as their primary goal while maintaining their routine epidemic prevention policies.
7.2 Second,the international community should establish a coordination mechanism to effectively solve the problem of vaccine availability in underdeveloped countries.
7.3 Third, the international community should actively explore the mechanism of mutual certification of vaccines.
7.4 Fourth and finally, the international community should continue to promote the COVID-19 vaccine as a “Global Public Goods” initiative.
Please Find us: Twitter: RDCYINST YouTube: RealRDCY LinkedIn: 人大重阳RDCY Facebook: RDCYINST Instagram: rdcyinst
Key Words: COVID-19; Boao; Report; RDCY




















































































 京公网安备 11010802037854号
京公网安备 11010802037854号





